RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ
# RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是一个开源的消息队列中间件,它实现了高级消息队列协议(AMQP)并提供可靠的消息传递机制。解决应用解耦、异步消息、流量削峰等问题。
# 相关概念
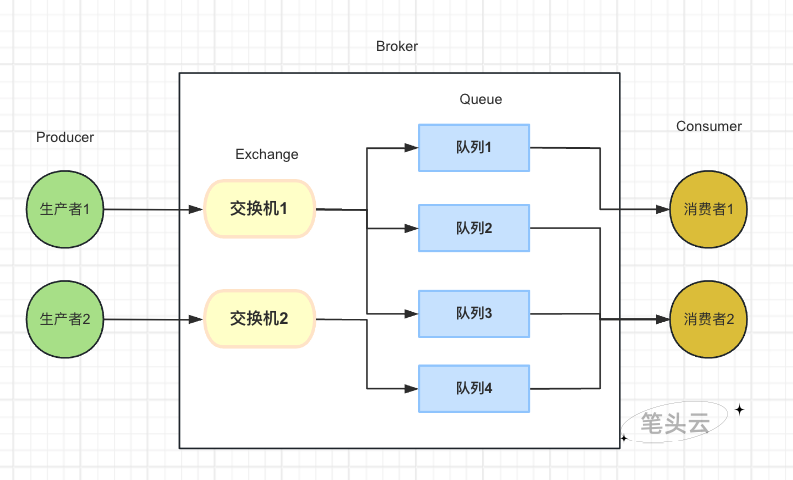
Producer: 消息生产者
Consumer: 消息消费者
Broker: RabbitMQ Server,接收和分发消息的应用
Exchange: 交换机,生产者将消息发送到交换机,交换机再转发到队列中
Queue: 队列,存放消息的容器
RoutingKey: 路由键,交换机根据路由键向队列投递消息
Binding: 绑定交换机和队列
- img: https://bitouyun.com/images/component/rabbitmq.png
link: https://bitouyun.com/images/component/rabbitmq.png
name: RabbitMQ
2
3
# docker安装
# 1. 安装网络 docker network create bitouyun
# 2. docker-compose.yml
# Copyright VMware, Inc.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: APACHE-2.0
version: '2'
services:
rabbitmq:
image: docker.io/bitnami/rabbitmq:3.12
ports:
- '4369:4369'
- '5551:5551'
- '5552:5552'
- '5672:5672'
- '25672:25672'
- '15672:15672'
environment:
- RABBITMQ_SECURE_PASSWORD=yes
- RABBITMQ_LOGS=-
volumes:
- 'rabbitmq_data:/bitnami/rabbitmq/mnesia'
volumes:
rabbitmq_data:
driver: local
networks:
default:
external: true
name: bitouyun
# 3. 启动容器
docker-compose up -d
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
常见问题
- User can only log in via localhost. 只能通过本地登录
新建用户并设置权限(已存在的用户会有问题)
docker exec -it rabbitmq_rabbitmq_1 /bin/sh # 进入容器
rabbitmqctl add_user 用户名 密码
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags 用户名 administrator
rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / 用户名 ".*" ".*" ".*"
# SpringBoot集成
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
username: 用户名
password: 密码
2
3
4
5
6
# 常用消息推送/接收模式
使用交换机转发消息时,有三种常用模式:直连模式(Direct)、广播模式(Fanout)和主题模式(Topic)。
不使用交换机时,有点对点模式和工作模式两种。
# Direct模式
直连模式,交换机根据路由键全字匹配寻找队列。
路由键:消费者绑定交换机和队列时,赋值路由键。
大致流程:队列绑定交换机,同时赋予RoutingKey(路由键),当消息通过生产者发送给交换机时,交换机根据RoutingKey(路由键)寻找绑定的队列并将消息发送到队列中。
Direct(直连模式)与Topic(主题模式)类似,区别是直连模式是全匹配路由键。
注意
启动消费者后创建交换机,绑定消息队列。
有多个消费者监听同一个队列时,轮询消费,不会重复消费。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送Direct消息 - RoutingKey(路由键): info
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/direct/send/info")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendDirectInfoMessage() {
log.info("发送Direct info消息");
Student student = new Student("001", "张三", 12);
// 参数: 交换机 路由键 消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE,
Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_INFO, JSON.toJSONString(student));
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
/**
* 发送Direct消息 - RoutingKey(路由键): error
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/direct/send/error")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendDirectErrorMessage() {
log.info("发送Direct error消息");
Student student = new Student("001", "张三", 12);
// 参数: 交换机 路由键 消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE,
Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_ERROR, JSON.toJSONString(student));
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 接收Direct消息
* Direct交换机绑定队列A,监听路由键为"info"的消息.
* bingds: 绑定交换机和消息队列 Queue: 队列, durable: 是否持久化, key: RoutingKey(路由键), Exchange: 交换机
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value =
@Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_A, durable = "true"),
key = {"info"},
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE, type = "direct")))
public void processDirectMessage1(String message) {
log.info("接收到Direct消息,RoutingKey:info,消息:{}", message);
}
/**
* 接收Direct消息
* Direct交换机绑定队列B,监听路由键为"error"的消息.
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value =
@Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_B, durable = "true"),
key = {"error"},
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE, type = "direct")))
public void processDirectMessage2(String message) {
log.info("接收到Direct消息,RoutingKey:error,消息:{}", message);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/**
* 常量类
*/
public final class Constants {
// Direct交换机
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "rabbitmq-direct-exchange";
// Direct消息队列A
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_A = "rabbitmq-direct-queue-a";
// Direct消息队列B
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_B = "rabbitmq-direct-queue-b";
// RoutingKey info
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_INFO = "info";
// RoutingKey error
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_ERROR = "error";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# Fanout模式
广播模式,消息发送到交换机,会分发到所有绑定的队列上,不处理RoutingKey,分发速度快。Fanout模式不需要RoutingKey,只需将交换机与队列进行绑定即可。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送Fanout消息
* 所有绑定的队列都收到消息,不需要RoutingKey。
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/fanout/send")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendFanoutMessage() {
log.info("发送Fanout消息");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sno", "002");
map.put("name", "李四");
map.put("age", 12);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", map);
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 接收Fanout消息
* Fanout交换机绑定队列A
* bingds: 绑定交换机和消息队列 Queue: 队列, durable: 是否持久化, Exchange: 交换机
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_FANOUT_QUEUE_A, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_FANOUT_EXCHANGE, type = "fanout")))
public void processFanoutMessage1(Map<String, Object> message) {
log.info("接收到fanout消息:{}", message.toString());
}
/**
* 接收Fanout消息
* Fanout交换机绑定队列B
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_FANOUT_QUEUE_B, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_FANOUT_EXCHANGE, type = "fanout")))
public void processFanoutMessage2(Map<String, Object> message) {
log.info("接收到fanout消息:{}", message.toString());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* 常量类
*/
public final class Constants {
// Fanout交换机
public static final String RABBITMQ_FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "rabbitmq-fanout-exchange";
// Fanout消息队列A
public static final String RABBITMQ_FANOUT_QUEUE_A = "rabbitmq-fanout-queue-a";
// Fanout消息队列B
public static final String RABBITMQ_FANOUT_QUEUE_B = "rabbitmq-fanout-queue-b";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# Topic模式
主题模式,RoutingKey(路由键)是字符串,用"."隔开,Topic(主题)与Direct(直连)类似,区别是路由键支持通配符,*:表示匹配一个词(必须出现),#:表示匹配0个或多个词。如:
beijing.# : 以beijing开头的路由键都会被匹配到,如beijing.news, beijing.weather, beijing.chaoyang.news。
*.news : 以news结尾的会被匹配到,如bejing.news。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送Topic消息
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/topic/send/{routingKey}/{message}")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendTopicMessage1(@PathVariable String routingKey,
@PathVariable String message) {
log.info("发送Topic消息,RoutingKey:{}, message:{}", routingKey, message);
// 发送消息,参数:交换机, 路由键, 消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 接收Topic消息
* Topic交换机绑定队列A
* 路由键: beijing.#, 以beijing开头的路由键都会被匹配,如:beijing, beijing.news, beijing.chaoyang.news
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_QUEUE_A, durable = "true"),
key = {Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_KEY_BJ}, // beijing.#
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, type = "topic")))
public void processTopicMessage1(String message) {
log.info("接收到Topic消息,RoutingKey: beijing.#, message:{}", message);
}
/**
* 接收Topic消息
* Topic交换机绑定队列A
* 路由键: *.news,以news结尾的路由键都会被匹配,如:beijing.news
* beijing.chaoyang.news, news都不会被匹配(*:匹配一个词)
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_QUEUE_B, durable = "true"),
key = {Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_KEY_NEWS}, // *.news
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, type = "topic")))
public void processTopicMessage2(String message) {
log.info("接收到Topic消息,RoutingKey: *.news, message:{}", message);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* 常量类
*/
public final class Constants {
// Topic交换机
public static final String RABBITMQ_TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "rabbitmq-topic-exchange";
// Topic消息队列A
public static final String RABBITMQ_TOPIC_QUEUE_A = "rabbitmq-topic-queue-a";
// Topic消息队列B
public static final String RABBITMQ_TOPIC_QUEUE_B = "rabbitmq-topic-queue-b";
// RoutingKey beijing.#
public static final String RABBITMQ_TOPIC_KEY_BJ = "beijing.#";
// RoutingKey *.news
public static final String RABBITMQ_TOPIC_KEY_NEWS = "*.news";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 点对点/工作模式
无交换机。
点对点模式:一个生产者、一个队列和一个消费者。
工作模式:一个生产者、一个队列和多个消费者,不会重复消费。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送消息
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/send/{message}")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendMessage(@PathVariable String message) {
log.info("发送消息:{}", message);
// 发送消息,参数: 队列名称, 消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_ROUTING_KEY_TEST, message);
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
@RabbitHandler // 接收队列消息方法
// 指定队列名称,如果队列不存在,则创建队列.
// @RabbitListener(queues = {"queueName"})如果队列不存在启动消费者会失败.
// durable: 是否持久化 autoDelete: 是否自动删除,最后一个消费者断开连接后,会自动删除.
// exclusive: 是否独享,私有的,true只有创建者可以使用此队列
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = Constants.RABBITMQ_ROUTING_KEY_TEST,
durable = "true", autoDelete = "false"))
public void processMessage1(String message) {
log.info("接收到消息1:{}", message);
}
// @RabbitHandler 可省略
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = Constants.RABBITMQ_ROUTING_KEY_TEST,
durable = "true", autoDelete = "false"))
public void processMessage2(String message) {
log.info("接收到消息2:{}", message);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/**
* 常量类
*/
public final class Constants {
// 路由键
public static final String RABBITMQ_ROUTING_KEY_TEST = "rabbitmq-routing-key-test";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 消息可靠性
使用消息队列后,可以业务解耦,但是业务链变长,造成消息丢失的场景也增加了(发送消息失败、消费消息失败和消息队列自身故障等)。
特别重要的数据能不用中间件尽量不用,尽管开启消息确认机制后,很大程度上保证了消息的准确送达,但是整体效率变低,吞吐量下降严重。不是非常重要的数据不建议用消息确认机制。
# 生产者消息确认
用来确认Producer(生产者)将消息发送到broker ,broker上的Exchange(交换机)再投递给Queue(队列)的过程中,消息是否成功投递。
- 添加配置
spring:
rabbitmq:
# 其它配置
# 确认消息已发送到交换机, springboot版本较低的话设置改成:publisher-confirms: true
publisher-confirm-type: correlated
publisher-returns: true # 确认消息已发送到队列
2
3
4
5
6
- 回调函数配置
注意
全局方式和局部方式只能选择一种。
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
// 全局方式
@Bean
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
// 开启Mandatory,才能触发回调函数
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
// 设置回调,消息推送到broker和queue失败都会调用此回调函数
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> {
if (!ack) {
// 发送到broker失败回调,可以先入库再做后续处理
log.error("发送到broker失败,correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause:{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
} else {
log.info("发送到broker成功,correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause:{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
}
});
// 消息转发到队列失败会调用此回调函数(成功不会回调)
rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(returnedMessage -> {
// 发送到队列失败回调,可以先入库再做后续处理
log.info("returnedMessage:{}", returnedMessage);
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
@Slf4j
@Service
public class SendMessageService implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback, RabbitTemplate.ReturnsCallback {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String message) {
log.info("发送消息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this);
rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(this);
}
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
if (!ack) {
// 发送到broker失败回调,可以先入库再后续处理
log.error("发送到broker失败,correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause:{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
} else {
log.info("发送到broker成功,correlationData:{}, ack:{}, cause:{}", correlationData, ack, cause);
}
}
@Override
public void returnedMessage(ReturnedMessage returnedMessage) {
// 发送到队列失败回调,可以先入库再后续处理
log.info("returnedMessage:{}", returnedMessage);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
结论
# 1. 推送到交换机失败, 触发ConfirmCallback回调函数, ack: fasle
# 2. 推送交换机成功,转发到队列失败, ConfirmCallback和ReturnCallback回调都触发, ack: true
# 3. 推送成功, 触发ConfirmCallback回调函数, ack: true
2
3
# 消费消息确认
消息的确认机制包括三种模式:AcknowledgeMode.NONE(自动确认)、AcknowledgeMode.AUTO(根据情况确认)和AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL(手动确认)。
自动确认,RabbitMQ将消息发出后即确认投递成功。当消费者没有处理成功这条消息时,就会丢失数据,这种情况可以使用try catch捕获异常再做后续处理。
手动确认,消费者收到消息后,手动调用basic.ack/basic.nack/basic.reject,RabbitMQ收到消息后,才确认投递成功。
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 手动模式
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_B, durable = "true"),
key = {"error"},
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE, type = "direct")),
ackMode = "MANUAL") // 手动模式
public void processDirectMessage3(String message, Channel channel,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long deliveryTag) throws IOException {
log.info("接收到Direct消息RoutingKey:error,deliveryTag:{},消息:{}", deliveryTag, message);
try {
// 业务处理
log.info("业务处理");
// basicAck: 成功确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否批量确认(为true时会确认小于当前投递号的消息)
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, false);
}catch (Exception e) {
// basicReject: 失败确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否重新入队列(true时重新进入队列)
channel.basicReject(deliveryTag, false);
// basicNack: 失败确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否批量确认,是否重新入队列
// channel.basicNack(deliveryTag,false,false);
// 业务处理异常,其它处理
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 死信队列
死信交换机、死信队列就是普通的交换机、队列,只不过接收、转发的消息是死信(Dead Letter)。
成为死信的条件:
- 消息被消费者拒绝(通过basic.reject 或 basic.nack),并且设置 requeue=false。
- 消息过期,因为队列设置了TTL(Time To Live)时间。
- 消息被丢弃,因为超过了队列的长度限制。
死信消息的生命周期:
- 消息推送到业务队列;
- 消费者消费消息时发生异常,进行reject/nack操作(或达到TTL、最大条数),投递到死信交换机中;
- 消息被死信交换机投递到死信队列;
- 死信队列的消费者消费死信。
死信应用场景:
较为重要的队列,确保未被正确消费的消息不被丢弃。将消息投递到死信队列中,对应的消费进行相应的处理(发送邮件、短信通知等)。
注意
绑定死信交换机时,之前创建的交换机需要删除后重新创建(或新建一个交换机)。
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送Direct消息 - RoutingKey: warn
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/direct/send/warn")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendDirectWarnMessage() {
log.info("发送Direct warn消息");
Student student = new Student("001", "张三", 12);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE_2, Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_WARN, JSON.toJSONString(student));
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 接收Direct消息
* 业务队列绑定业务交换机,并绑定死信交换机,死信路由键
* 手动确认,,TTL过期,达到最大长度,放入死信交换机
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_B_2, durable = "true",
arguments = {@Argument(name = "x-dead-letter-exchange", value = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE), // 绑定死信交换机
@Argument(name = "x-dead-letter-routing-key", value = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY) // 绑定死信队列路由键
// @Argument(name = "x-message-ttl", value = "10000", type = "java.lang.Long"), // TTL过期时长,
// @Argument(name = "x-max-length",value = "100") // 队列达到最大长度
}),
key = {"warn"},
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE_2, type = "direct")),
ackMode = "MANUAL")
public void processDirectMessage4(String message,Channel channel,@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long deliveryTag) throws IOException {
log.info("接收到Direct消息RoutingKey:warn,消息:{}", message);
try {
// 业务处理
log.info("业务处理");
int i = 2 / 0; // 异常
// basicAck: 成功确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否批量确认(为true时会确认小于当前投递号的消息)
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, false);
}catch (Exception e) {
// basicReject: 失败确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否重新入队列(true时重新进入队列,false时进入死信交换机)
channel.basicReject(deliveryTag, false);
// basicNack: 失败确认, 参数: 投递序号,是否批量确认,是否重新入队列(false时进入死信交换机)
// channel.basicNack(deliveryTag,false,false);
// 业务处理异常,其它处理
}
}
/**
* 接收死信消息
* 死信队列绑定死信交换机,设置路由键
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE, durable = "true"),
key = {Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY},
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE, type = "direct")))
public void processDirectMessage5(String message){
log.info("接收到Direct 死信消息,消息:{}", message);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public final class Constants {
// Direct交换机
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_EXCHANGE_2 = "rabbitmq-direct-exchange_2";
// Direct消息队列B
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_QUEUE_B_2 = "rabbitmq-direct-queue-b_2";
// RoutingKey warn
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_KEY_WARN = "warn";
// Direct死信交换机
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "rabbitmq-direct-dead-letter-exchange";
// Direct死信队列
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE = "rabbitmq-direct-dead-letter-queue";
// Direct死信队列路由键
public static final String RABBITMQ_DIRECT_DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY = "rabbitmq-direct-dead-letter-routing-key";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 延时队列
延时队列是用来存放需要在指定时间被处理的元素的队列。
应用场景:
- 关闭未在指定时间内支付的订单。
- 在预定会议开始前10分钟通知参会人员。
- 外卖配送超时提醒,提前10分钟提醒外卖小哥。
实现方式:
- rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange 插件,安装插件,发送消息时在消息头设置延迟时间,实现简单。
- 死信交换机+TTL超时时间,配置交换机、路由键和TTL超时时间,不绑定消费者,等到达超时时间时,消息被投递到死信队列,由死信队列的消费者消费消息。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* rabbit config
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
// 绑定延时队列、延时交换机
@Bean
public Declarables declarables() {
Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>();
args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", "delay_dead_letter_exchange"); // 绑定死信交换机
args.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "delay_dead_letter_routing_key"); // 绑定死信路由键
args.put("x-message-ttl", 10000); // 设置超时时间
Queue delayQueue = new Queue("delay_queue", true, false, false, args);
DirectExchange delayExchange = new DirectExchange("delay_exchange");
Binding binding = BindingBuilder.bind(delayQueue).to(delayExchange).with("delay");
return new Declarables(delayQueue, delayExchange, binding);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitMQController {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 发送Direct延时消息 - RoutingKey: delay
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/direct/send/delay")
public ResponseEntity<?> sendDirectDelayMessage() {
log.info("发送Direct delay消息");
Student student = new Student("001", "张三", 12);
// 参数: 延时交换机, 路由键, 消息内容
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("delay_exchange", "delay", JSON.toJSONString(student));
return ResponseEntity.ok("发送成功");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RabbitMQConsumer {
/**
* 延时队列消费者
* 消费死信队列消息
*/
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "delay_dead_letter_queue", durable = "true"),
key = {"delay_dead_letter_routing_key"}, // 路由键
exchange = @Exchange(name = "delay_dead_letter_exchange", type = "direct")))
public void processDirectMessage7(String message) {
log.info("消费延时队列消息,消息:{}", message);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group